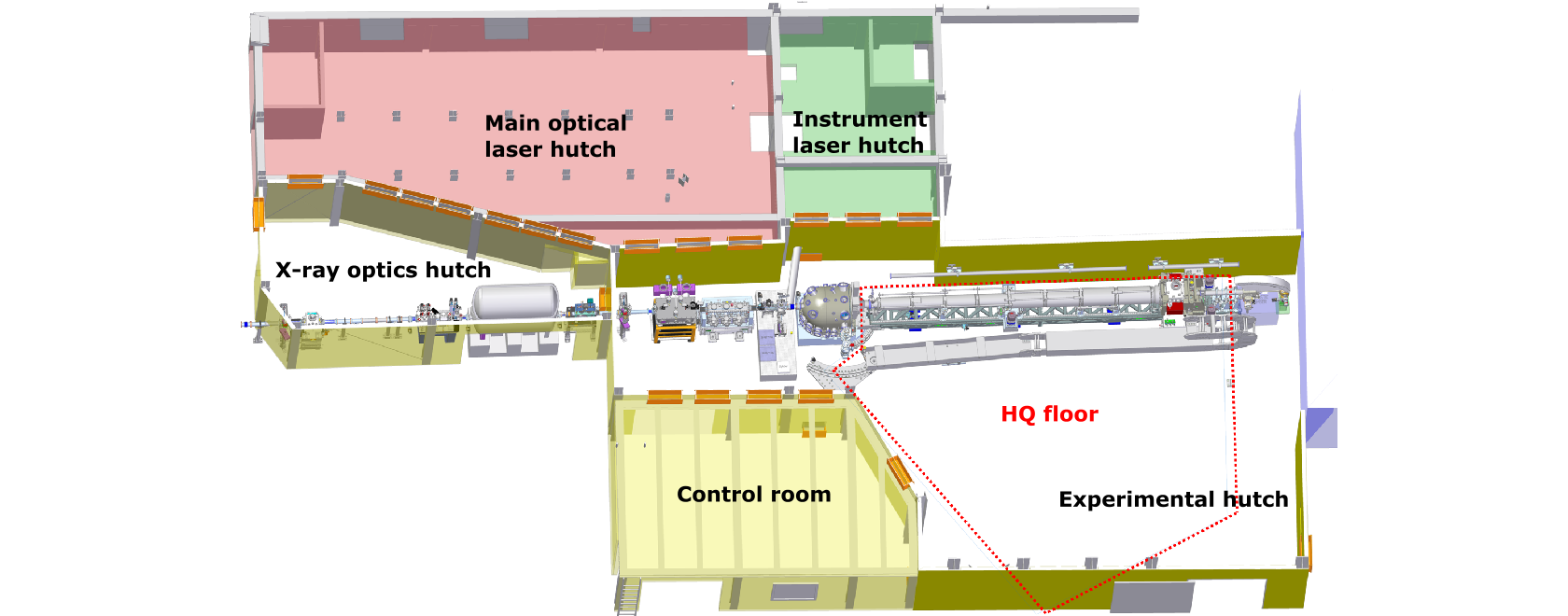
The scope of the MID instrument are material science experiments using the unprecedented coherent properties of the X-ray laser beams of the European XFEL. The scientific applications reach from condensed matter physics, studying for example glass formation and magnetism, to soft and biological material, such as colloids, cells and viruses. Several X-ray scattering and imaging techniques will be offered taking advantage of coherence, flux, and ultrashort duration of the X-ray pulses.
Imaging
Imaging covers a broad range of techniques and scientific fields, from classical phase-contrast tomography to coherent X-ray diffraction imaging (CXDI) and with applications, e.g. in strain imaging inside nanostructured materials to bio-imaging of whole cells. In many cases the aim is to obtain a 3D representation of the investigated structure. By phase retrieval methods it is possible to pass from the measured diffraction patterns in reciprocal space to a real space visualization of the scattering object.
Dynamics
Complex nanoscale dynamics is an ubiquitous phenomenon of fundamental interest at the forefront of condensed matter science, and comprises a multitude of processes from visco-elastic flow or dissipation in liquids and glasses to polymer dynamics, protein folding, crystalline phase transitions, ultrafast spin transitions, domain wall dynamics, magnetic domain switching and many more. The extremely brilliant and highly coherent X-ray beams will open up unseen possibilities to study dynamics in disordered systems down to atomic length scales, with timescales ranging from femtoseconds to seconds.
- EXAFS
- Crystallography
- Surface diffraction
- Time-resolved studies
- Coherent diffractive imaging
- Coherent scattering
- Elastic scattering
- Magnetic scattering
- Resonant scattering
- Small angle scattering
- Time-resolved scattering
- Wide angle scattering
- Physical Chemistry
- Biophysics
- Knowledge based multifunctional materials
- Metallurgy
- Other - Material Sciences
- Technique Development - Material Sciences
- Atomic & molecular physics
- Dynamics
- Hard condensed matter - structures
- Nanophysics & physics of confined matter
- Optics
- Other - Physics
- Soft condensed matter physics
- Surfaces, interfaces and thin films
- Technique Development - Physics
- n/a
- n/a
- n/a